Donald Trump has never been mistaken for an environmentalist, having long called the climate crisis a “giant hoax” and repeatedly lauding the supposed virtues of fossil fuels.
But the US president’s onslaught upon the natural world in this administration’s first 100 days has surprised even those who closely charted his first term, in which he rolled back environmental rules and tore the US from the Paris climate agreement.
This time, the mantra “drill, baby, drill” has been used to justify a hyperactive series of actions to reverse rules designed to protect clean air and water, open up vast tracts of land, ocean and even the seabed to mining, fire federal scientists en masse and downgrade the federal response to the disasters that stem from a warming world.
Trump’s Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is attempting to roll back toxic regulations that were calculated to save an estimated 200,000 Americans’ lives in the years ahead, his Department of the Interior is looking to shrink national monuments and his scientific agencies are degrading the basic data collection required for climate assessments and even weather forecasts.
This burst of activity faces a barrage of legal action, with the courts already taking a dim view of the administration’s attempts to skirt usual practice in its haste to deregulate. Even with a rightwing-dominated supreme court, many of these executive orders are expected to founder.
However, the US must accelerate efforts to cut emissions if climate goals are to be met, half of Americans still have to endure unsafe air and endangered species and public lands face pressure from a changing climate. The next few years will see little remedy to these growing problems from the White House.
“The pace of announcements may slow at some point but the pressure on our regulatory system and our democracy will not only continue, but ramp up,” said Michael Burger, a climate law expert at Columbia University.
“The result will be fewer environmental protections and more people suffering the public health consequences of more pollution. It’s that straightforward.” Oliver Milman
Historic rollbacks of environmental regulations
What has the administration done:
-
Taken more than 140 actions to roll back environmental rules and push for greater use of fossil fuels.
-
Set about rewriting regulations that limit pollution from cars, trucks and power plants.
-
Officially reconsidering whether greenhouse gases actually cause harm to public health.
-
Legally targeted states that have their own laws on tackling the climate crisis.
-
Speeded up environmental reviews of drilling projects, from years to just a few weeks.
-
Winding back water efficiency standards for showers and toilets and halting a phase-out of plastic straws

Analysis and reaction: When campaigning for president, Donald Trump promised to torch environmental regulations if fossil fuel companies were able to donate enough money to propel him to the White House. He has set about fulfilling this pledge in dizzying fashion.
By the Guardian’s count, Trump’s administration has taken more than 140 actions to weaken or rescind environmental rules and to escalate the use of fossil fuels in his first 100 days – more than all of the rollbacks of his entire first term.
The drumbeat of this effort, largely via a blizzard of executive orders and agency memos, to eviscerate rules designed to protect Americans’ air, water and a livable climate, has been relentless. “What we’ve seen in this first 100 days is unprecedented – the deregulatory ambition of this administration is mind-blowing,” said Burger of Columbia University.
In a single day in March, Trump’s EPA launched 31 different actions to refashion pollution laws for cars, trucks and power plants and even re-evaluate whether greenhouse gases harm public health – a key finding that underpins US climate laws. It was a “dagger to the heart of the climate religion”, according to Lee Zeldin, the EPA administrator.
Zeldin has repeatedly touted the EPA’s record during the first 100 days, with the agency publishing a list of 100 environmental actions, including the cleanup of toxic waste and the testing of chemicals.
But the administration has also sought to ease restrictions upon coal plants dumping their toxic ash and mercury and to scale back a plan to prevent states from wafting their pollution to their neighbors. Consideration of the climate crisis has been removed from federal spending decisions and disaster recovery, pipeline safety standards are to be relaxed and environmental permit approvals speeded up from years to just weeks.
Places of refuge for nature and carbon storage, such as oceans and national forests, will be opened up for the extraction of fish and timber while endangered species laws are set to be upended and, if the administration gets its way, essentially neutered.
Not content with the reorientation of the federal government’s response to the climate crisis, Trump has ordered his Department of Justice to target states that have their own climate laws. He has also ordered the expiration of environment and energy regulations across 25 different laws, usually a responsibility of Congress.
Trump has even used the power of his office to attend to his own fixations around shower water pressure, which he considers too weak, and paper straws, which he dislikes compared with the plastic alternative. “There doesn’t seem to be any strategy to this but I feel like I have policy whiplash,” said Gina McCarthy, who was Joe Biden’s top climate adviser.
“We see an administration that doesn’t care about these things and is all about the whims of President Trump. Executive orders are not laws, though, and we spend a great deal of time focusing on them when most of them are highly illegal and won’t go anywhere.” Oliver Milman
Trump’s ‘drill, baby, drill’ agenda
What the administration has done:
-
Trump signed executive orders to ease restrictions on fossil fuel extraction and exports, pledging to “unleash American energy”.
-
He tapped fossil fuel-supporting appointees to head up crucial federal agencies, including Chris Wright, a former fracking CEO, for energy secretary; Doug Burgum, former Republican governor of North Dakota – the third largest oil and natural gas producer in the country – to lead the interior department (DOI); and Lee Zeldin, a former Republican congressperson to head the EPA.
-
Trump offered the fossil fuel industry – which lavished record levels of donations on him and Congress – an exemption from the tariffs he presented in April (and which he placed on pause shortly thereafter).
Analysis and reaction: Aru Shiney-Ajay, executive director of the youth-led environmental justice group Sunrise Movement said: “Donald Trump’s actions on climate are part of a ruthless agenda to prop up big oil and reward the billionaires bankrolling his campaigns. Big oil’s bribe paid off.”
Trump’s loyalty to the fossil fuel industry has not, however, shielded fossil fuel companies from the fallout of his erratic policymaking. The domestic oil industry is currently facing the some of the lowest prices for crude it has seen in years. The Dow Jones’s US Oil and Gas Index, which tracks 42 fossil fuel companies, plummeted by more than 15% since Trump announced the tariffs on 2 April, sinking to its lowest level since 2022, before a slow, partial rebound.

Meanwhile, Trump’s tariffs have already begun driving up the costs of oil production, with new taxes on steel and aluminum inflating the costs of building fossil fuel infrastructure. And his calls to “drill, baby, drill” have raised concerns about oil demand, since an increase in supply could push down prices, thereby limiting profit.
Though the oil industry has publicly praised Trump, they have quietly showed they are anxious about the economic implications of his policies. In a recent anonymized survey by the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas, for instance, fossil fuel executives brazenly criticized Trump. “The administration’s chaos is a disaster for the commodity markets,” one oil boss said. “‘Drill, baby, drill’ is nothing short of a myth and populist rallying cry. Tariff policy is impossible for us to predict and doesn’t have a clear goal. We want more stability.”
At a major Texas oil and gas conference in May, fossil fuel top brass echoed these criticisms.
Though the Trump administration has not ended the chaos created by its policies, it has given big oil other gifts. In recent weeks, for instance, Trump signed an executive order instructing the Department of Justice to “stop the enforcement” of state climate laws forcing polluting companies to pay for climate damages, and also targeting dozens of lawsuits that accuse big oil of intentionally covering up the climate risks of their products. Dharna Noor
Hollowing out agencies including Noaa, Fema and DOI
What has the administration done
-
Sweeping cuts to federal agencies on the forefront of the climate crisis, including the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (Noaa), the Federal Emergency Management Agency (Fema), the DOI and the Department of Agriculture (USDA), and widespread firings of climate scientists and regulation experts.
-
Withdrawal from contracts and canceled grant funding; datasets pulled from public-facing websites; funding for regional climate centers suspended.
-
National Climate Assessment contract canceled; hundreds of experts dismissed.
-
Executive order to expedite deep-sea mining for minerals.
-
Plans to dismantle a key Fema disaster preparedness program.
-
Weather balloon launches stopped due to staff shortages.
-
Censorship of climate-related words, flagged in studies, contracts and agency documents/websites.
-
Plans to drain funding for climate, weather and ocean laboratories.
Analysis and reaction: Trump wasted no time before he unleashed an all-out assault on environmental science, gutting the federal agencies positioned on the frontlines of the climate crisis, firing hundreds of researchers, staffers and forecasters and pulling public access to critical resources and data.
Vital work to understand, prepare and respond to changes caused by global heating has slowed or stopped as teams try to navigate the chaos, while the threat of more severe budget cuts and political crackdowns lingers. The moves largely bypassed input or oversight from Congress as Trump used executive orders and actions undertaken by the billionaire Elon Musk-led “department of government efficiency”, even on budget issues typically governed by the legislative branch.

Thousands of federal workers were culled from the ranks across the country’s premier scientific agencies – including at Noaa and Nasa – and in roles across the government that typically facilitate regulatory process or research. Many of those fired were probationary employees, a classification applied to the first year, or sometimes two, in a position.
The widespread firings were challenged in court, forcing the administration to rehire workers and put them on administrative leave, only to fire them again when legally in the clear. In the end, at least 121,000 federal workers were fired, leaving significant holes in their wake.
Thousands more workers have opted to take offers of early retirement or voluntary separations. At Noaa alone, roughly 27,000 years of collective experience was lost, according to Craig McLean, the former director of Noaa research.
“We lost our promising new talent in the probationary firings and now we’ve lost our institutional knowledge,” a Noaa employee said of the resignations, asking for anonymity out of fear of retribution.
While the losses are expected to have a profound effect on the American public, the impact will be felt globally too.
Among the hundreds of positions lost were workers who track El Niño-La Niña weather patterns around the world, people who model severe storm risks, and scientists contributing to global understanding of what could happen as the world warms.
“I want to emphasize that this blunt smashing of federal agencies is limiting the ability of our nation to respond not only now, but in the future,” said Dr Gretchen Goldman, president of the Union of Concerned Scientists. “It’s dismantling the very infrastructure by which we collect data, foster expertise and collaboration, and have the people and processes in place to take action.”
Already, the staff shortages have hampered data collection and field offices have had to stop deploying tools that gather essential intel.
“The effects may not be obvious until there is a major tornado outbreak, or a hurricane landfall downwind, that doesn’t go so well,” said climate scientist Daniel Swain, who spoke about the gravity of this issue during a recent broadcast on YouTube. But, he said, the actions taken in the first 100 days were just the beginning.
“What we have seen so far is just the tip of the iceberg,” he said, noting recently leaked budget documents that outline the president’s plans to continue gutting climate science-focused federal work. If the administration has its way, he said, “it would probably spell the end of most publicly funded climate research in the United States”. Gabrielle Canon
Public lands targeted
What has the administration done
-
Rescinded protections for hundreds of millions of acres of federal waters.
-
Initiated major changes to National Environmental Policy Act (Nepa) regulations that require federal projects consider environmental impacts and enable public oversight/comment, severely reducing the often years-long environmental impact process to 28 days.
-
Ordered the end of American Climate Corps jobs that create climate and public lands-supporting positions.
-
Plans to fast-track controversial deep-sea mining and accelerating approvals for mining, drilling, and fossil fuels extraction on public lands..
-
Proposed rolling back protections in the Endangered Species Act.
-
Plans to rescind Bureau of Land Management rules that protect millions of acres in Alaska and across the US west; planned repeal of BLM Public Lands Rule.
-
Emergency situation determination issued by the USDA to open logging on more than 100m acres of national forests and an executive orders to increase and accelerate logging on federal lands. And revoked a Biden order that protected old-growth forests.
-
Joint taskforce between DOI and the Department of Housing and Urban Development to examine federal lands for housing development as the administration pushes for the sell-off of public lands.
Analysis and reaction: Trump may be one of the very few Americans who doesn’t cherish the country’s public lands. Voter support for these roughly 640m acres – forests and deserts, parks and monuments among them – is stalwart and one of the few issues bridged by an otherwise vast political divide.
But even with broad popularity and a rapidly escalating interest in outdoor recreation that’s fueled both local economies and international tourism, the administration has made it a priority to shrink land management agencies, reduce protections once governed by them and possibly even diminish the holdings of lands under federal jurisdiction.
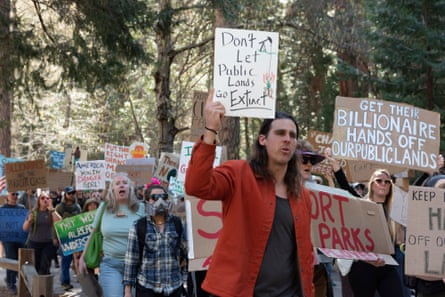
Thousands of employees were fired or took deals to leave, and agencies are struggling to hire seasonal employees who typically run operations during the busiest seasons. Still, more cuts are being planned as Trump seeks to reshape the federal government. Reports found the Department of Interior has plans to cull roughly 25% of its workforce, and employees at the US Forest Service are bracing for a broad reduction in force that has yet to be detailed. The National Park Service alone has suffered a 13% reduction in staff already.
Sweeping firings left behind gaping holes in an already short-staffed workforce at parks and forests, leaving some departments with workforce levels typically seen during government shutdowns according to some experts.
Toilets, trash and overgrown trails may become a common feature in highly trafficked areas, along with increasing risks of trampled conservation areas, a lack of capacity for the study of threatened plants and animals, and lost support that ensures safety measures are followed. Visitation has surged in recent years, adding new strains on ageing infrastructure and more opportunities for injuries and wildlife conflicts, as dangers from extreme conditions fueled by the climate crisis continue to mount.
“Scientists who should be doing their job tracking the wildlife and the ecosystems in these parks, are being told they have to take restroom cleaning shifts,” said Aaron Weiss, the deputy director for the Center for Western Priorities. “That’s incredibly important in parks,” he added, “but we shouldn’t be assigning those jobs to scientists because Doge has fired all the custodial staff.”
It’s not just about recreation, though. The administration has also made moves to open the country’s holdings of conservation areas, protected habitats and wilderness to extraction and development. There have been a series of orders from the administration that call for increased logging, fossil fuels leases, and mining as Trump pushes for expanding industry access.
Ben Vizzachero, a federal worker who initially lost his job during the federal firing spree but who was later brought into his position said the outlook still remained bleak for US public lands. “The Trump administration is waging a campaign of bullying and harassment, trying to shrink the federal workforce by any means,” he said, noting that removing regulators and regulations will “open lands for mining, logging, drilling, and other destruction”.
These sweeping changes and the threats to public lands come as they continue to be widely supported and cherished by the American people. “The fight to protect our public lands is embedded within the fight for our democracy itself.” Gabrielle Canon
Gabrielle Canon
Cancelling environmental justice schemes, and hitting US farmers
What has the administration done
-
Trump immediately rescinded a slew of executive orders that directed federal agencies to prioritize tackling environmental racism and other injustices – including one dating back more than 30 years.
-
A separate executive order focused on ending government-sponsored diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI) initiatives and so-called “illegal DEI” efforts in the private sector also targeted environmental justice by wrongly conflating the two. This called for the closures of all environmental justice offices and positions in the federal government – including the office of environmental justice and external civil rights which was created to support EPA efforts to help improve access to clean water, air and land in communities disproportionately affected by environmental pollution, as well as enforce federal civil rights laws.
-
Mass layoffs in the EPA, USDA and health and human services department which will disproportionately hit access to adequate, clean and affordable food, water, air and energy for low-income and rural communities.
-
Freezing the Biden-era Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund – more than $20bn of competitive grants available to states, cities, tribes and other eligible groups to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, particularly in areas most affected by climate crisis and excluded from mainstream finance.
-
Terminating climate and conservation grants to US farmers including the Biden-era five-year $3.2bn real-life study into the effectiveness of conservation practices such as cover cropping for commodity farms.

Analysis and reaction: From day one of Trump 2.0, the president has revealed his intention to willfully conflate environmental justice – efforts to acknowledge and correct decades of harm caused by placing polluting factories, landfills, fossil fuel infrastructure and highways in low-income and Indigenous people and communities of color – with what he and his allies believe to be woke, anti-white DEI policies that proliferated in response to the BLM movement.
Citing Trump’s crusade against DEI, the justice department terminated a two-year investigation into a petrochemical plant in LePlace, Louisiana, accused of emitting extraordinarily high levels of the cancer-causing chemical chloroprene into the majority Black community. Then, in an unprecedented move, his justice department terminated a 2023 landmark settlement with the state of Alabama requiring health authorities to provide the majority-Black Lowndes county with basic sewage and sanitation services – which an earlier investigation found had been denied for decades due to environmental racism. Several other consent decrees involving egregious polluters are feared to be under threat.
Not to be outdone, Robert F Kennedy Jr, secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), dismantled the office and fired the entire staff at the Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (Liheap). States were still waiting for about $380m to be disbursed this year, when the bipartisan program that helps low-income Americans struggling to pay energy bills so they don’t die from the extreme heat or cold was disbanded. In a leaked HHS budget for 2026 seen by the Guardian, Liheap was terminated – which unless revived will increase heat and cold deaths in the richest country in the world.
The $20bn Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund, and the portal, has been frozen on and off since February, causing chaos and uncertainty for recipients as this makes its way through the courts. The money was appropriated by Congress through the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act and finalized before the election, and it is widely agreed (outside Trump world) that the fund cannot legally be cancelled without legislation. The fear is that the Republican-majority Congress will succeed in pushing this through in the continuing resolution for the 2025 budget, which should be passed in May.
“The administration is trying to make it so difficult that people will give up, but our quest for environmental justice [has been waged] for 40 years and we will not stop now,” said one veteran environmental justice leader who asked not to be named in fear that his organization, a recipient of the fund, would be targeted. “The climate crisis is real; environmental racism is real. Those are the facts.” Nina Lakhani
Tearing up US global climate pledges
What has the administration done
-
Pulled out of the 2015 Paris accords, which the Biden administration rejoined in 2021 – four years after Trump first withdrew the US from the global climate mitigation pact.
-
Withdrew the US from the loss and damage fund – a global agreement under which the developed countries most responsible for the climate crisis pledged to partly compensate developing countries for irreversible harms caused by global heating.
-
The EPA missed the annual 15 April deadline to submit data on US greenhouse gas emissions to the United Nations – the first time in 30 years.
Analysis and reaction: The US is currently the second biggest greenhouse gas emitter, so withdrawing from the Paris agreement and its legally binding commitment to reduce emissions will further weaken global efforts to slow global heating – with catastrophic consequences for communities vulnerable to climate shocks in the US and globally. It takes a year for the withdrawal to go into effect, but missing the 15 April emissions reporting deadline, which never happened even during Trump’s first term, has raised suspicion that this administration is willing to violate international rules and could be preparing to exit from the entire UNFCCC.

Another major concern is climate finance. As the world’s biggest economy (and worst historical polluter), the US has been a major, albeit inadequate, contributor to global climate funds to help developing countries that are not responsible for global heating in their climate mitigation and adaptation efforts. It has already pulled out of the loss and damage fund, adopted at the Cop28 UN summit in 2023 after years of diplomatic and grassroots advocacy – and despite US efforts to block it. The US has long obstructed progress on global climate action and had pledged a measly $17.5m (£13.5m) to the fund; the cynical move to withdraw from loss and damage efforts – while bolstering fossil fuel production – was widely condemned by the global south.
Harjeet Singh, a climate activist and founding director of the India-based Satat Sampada Climate Foundation, said: “As the largest historical emitter, the United States bears a significant share of the blame for the climate adversities affecting vulnerable populations worldwide. The decision by the Trump administration exemplifies a longstanding pattern of obstruction by the US government in securing necessary finance for addressing climate impacts, [and] undermines global efforts to deliver climate justice.” Nina Lakhani

 6 hours ago
5
6 hours ago
5













































